CCSS™
Our CCSS™ Auditor and Implementor Training is Now available!
Learn more about the CCSS and how to get your system(s) certified.
FAQs
What is the CCSS
CCSS is a standard for securing cryptocurrency systems
CryptoCurrency Security Standard (CCSS) is a set of requirements for all information systems that make use of cryptocurrencies, including exchanges, web applications, and cryptocurrency storage solutions. By standardizing the techniques and methodologies used by systems around the globe, end-users will be able to easily make educated decisions about which products and services to use and with which companies they wish to align.
The CCSS is updated regularly to keep pace with the rapidly evolving cryptocurrency industry. The latest version, 9.0, was published on December 17, 2024.
CCSS is designed to complement existing information security standards (i.e. ISO 27001:2013) by introducing guidance for security best practices with respect to cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. CCSS is not designed to substitute or replace these standards; in fact, following the CCSS to the letter while ignoring standards like ISO 27001:2013 will likely lead to compromise. CCSS is a cryptocurrency standard that augments standard information security practices. As with any standard, knowledgeable and experienced security professionals and/or auditors are necessary when implementing any information system to ensure coverage of all classes of attack as well as the appropriate handling of all potential risks.
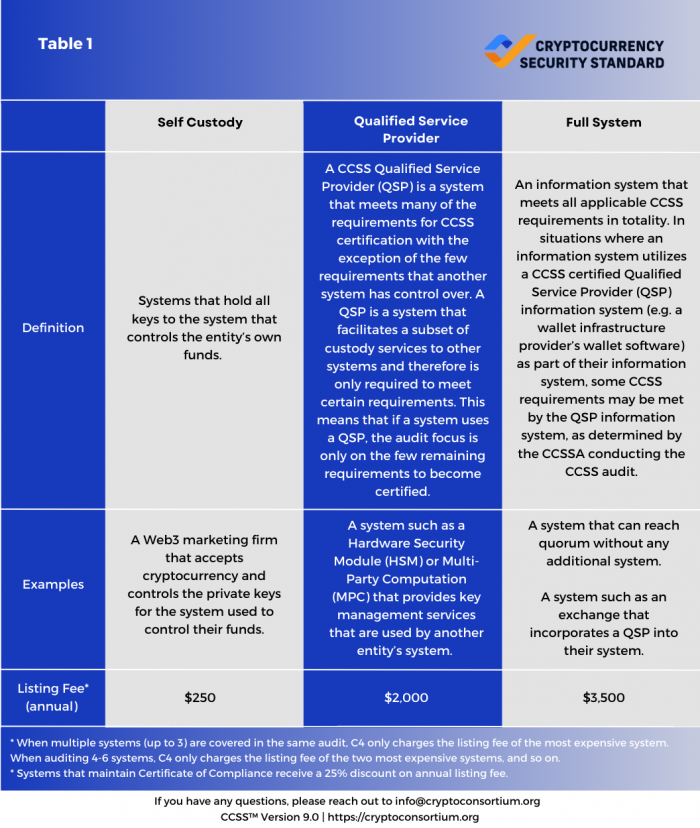
There are different types of cryptocurrency systems, and an Entity can have multiple types of systems. Entities are not certified, but rather systems are certified. Systems can be certified as CCSS Level 1, 2, or 3 with increased security as the levels increase. Systems fall into 3 buckets. Self-Custody, Qualified Service Provider (QSP), and Full System.
A self-custody system has sole control of the private keys that controls that entity’s own funds. Self Custody systems do not have control over customer funds.
A CCSS Qualified Service Provider (QSP)'s system meets many of the requirements for CCSS certification with the exception of the few requirements that another system has control over. A QSP is a system that facilitates a subset of custody services to other systems and therefore is only required to meet certain requirements. This means that if a system uses a QSP, the audit focus is only on the few remaining requirements to become certified.
A CCSS Full System is a system that meets all applicable CCSS requirements in totality. In situations where a system includes a QSP system as part of their system, some CCSS requirements may be met by the QSP system, as determined by the Cryptocurrency Security Standard Auditor (CCSSA).
Documentation
Our CryptoCurrency Security Standard (CCSS) Auditor Exam is now ready! Learn more about the exam here.
How to start a CCSS Audit
Certified CCSS Systems have been independently evaluated and audited against 41 aspect controls of the CryptoCurrency Security Standard. Systems that earn Level 1, Level 2, or Level 3 designations have proven they are robust, resilient, and rooted in best practices. Learn more about the CCSS and how to get your system(s) certified below.
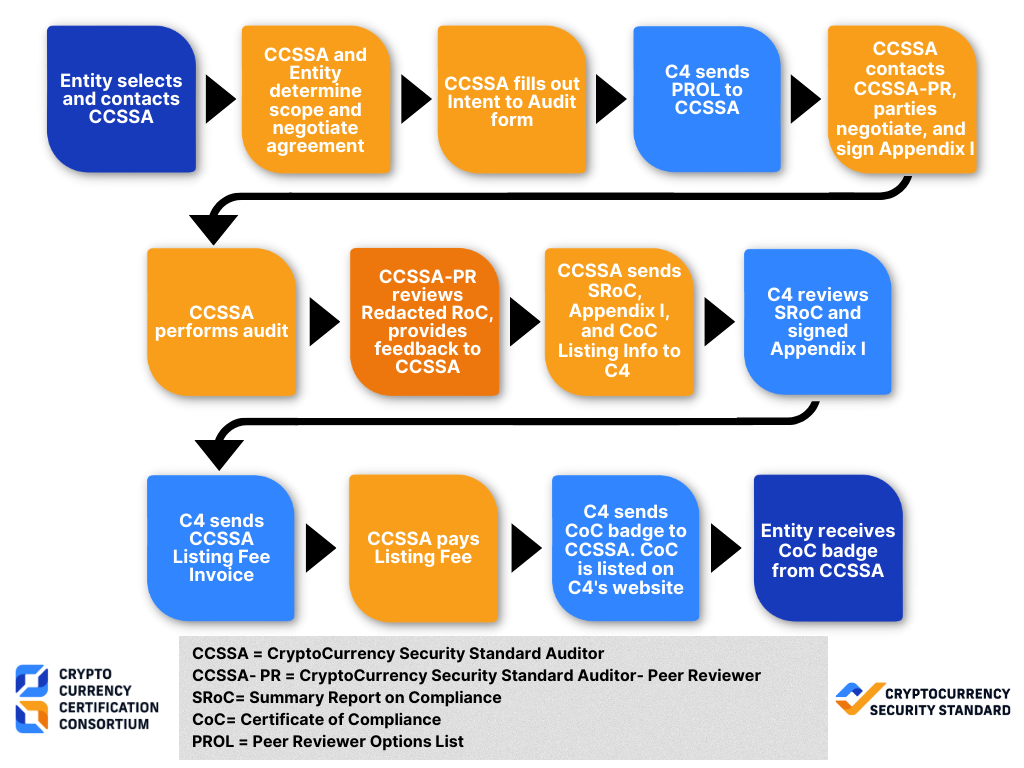
The first step to getting audited is to select a CCSSA. You can search our currently certified CCSSAs here. Entities then contact and negotiate with the CCSSA of their choosing. Please note that while these individuals have proven their knowledge of the CCSS, C4 does not endorse specific CCSSAs. It is imperative that entities follow best practices for selecting an auditor.
All CCSS audits cover a period of time prior to audit completion and will test the operating effectiveness of the control over this period of time. Audits are designed to be performed at least annually and cover the preceding 12 month period. All audits performed by CCSSAs are reviewed by a CCSSA-Peer Reviewer before C4 certifies an entity. Any dispute arising out of the peer review process shall be arbitrated by the CCSS Steering Committee.
The CCSSA is responsible for ensuring all data related to the audit is transmitted and stored in a secure manner for the duration of the Certificate of Compliance (CoC) and as legally required in the jurisdiction of the audit. C4 will not view documentation of evidence outside the Summary Report on Compliance (SRoC). The CCSS steering committee shall review evidentiary documentation in the case of a peer review dispute.
.
What is a CryptoCurrency Security Standard Auditor (CCSSA)?
A CryptoCurrency Security Standard Auditor is an expert in the CCSS. CCSSAs are able to apply the CCSS standard to any information system that uses cryptocurrencies, calculating a grade for the system according to the CCSS.
CCSSAs must avoid any potential conflict of interest. This may include current or previous employment, familial relationships, financial interest (such as tokens or equity held), or any other matters that may constitute a conflict of interest.
Learn how to become a CCSSA here.
What is the cost of a CCSS audit?
Audit fees will be determined between the CCSSA and the entity. It is the responsibility of the CCSSA to ensure sufficient time to complete the audit is reflected in the agreed upon fees.
Audit fees must also include the Listing Fee and the CCSSA-PR’s fee, as determined between the CCSSA and the CCSSA-PR. The CCSSA-PR’s fee will be forwarded to the CCSSA-PR by the CCSSA. C4 will send an invoice for the Listing Fee to the CCSSA after approving the SRoC.
The listing fee, paid by the audited system’s entity to the CCSSA, is based on Table 1.
Who manages the CCSS?
The standard is maintained by the CCSS Steering Committee. The committee's mission is to ensure the standard continues to remain up-to-date with industry best practices and remain neutral. Current CCSS Steering Committee members are (in alphabetical order):

S. Dirk Anderson
Founder & Chief Strategist at Imagine Crypto, LLC, CCSS Steering Committee Chair

Petri Basson
Founder - HASH consulting

Marc Krisjanous
Associate Director of Audit at SixBlocks Audit

Jameson Lopp
Co-Founder and Chief Security Officer of Casa

Joshua McDougall
President, Slow Ninja

Michael Perklin
Security Expert and Chairman of the Board, CryptoCurrency Certification Consortium (C4)

Ron Stoner
Head of Security at Botanix Labs
