
A Beginners Guide to Cryptocurrency Wallets
Before we discuss types of wallets, it is a good idea to first have a general understanding of what cryptocurrency is and why it is important.
Many cryptocurrencies work by utilizing public networks and ledgers (a ledger is a record of financial transactions) called blockchains. At its simplest level, cryptocurrencies let you send and receive value to and from anyone in the world, using only an Internet connection. What makes it so revolutionary is that, unlike every other tool for sending money over the Internet, it works without the need to trust or gain the permission of a centralized authority. Which makes it the world’s first public and decentralized digital payments infrastructure!
Public in this case, means no single entity owns or controls the ledger, nor can it be changed. This decentralized ledger reduces the risk for corruption, fraud and manipulation and decreases time, cost and limitations associated with the use of such entities.
Feeling confused? Don’t worry, we will provide additional content to help you understand this technology. For now, this is enough to set the framework for this wonderful, and sometimes weird, journey!
How Do I Get Started?
As mentioned above, cryptocurrencies use blockchain technology. All that is needed is an address on the Blockchain to receive payments digitally.
Given this, the first step to starting your cryptocurrency journey will be to choose and set-up a wallet, which will create an address on your chosen blockchain.
What is a wallet and why exactly do I need one? Let’s start with the why.
Why Do I Need a Wallet?
Just like you need an email application like Outlook or Gmail to manage your email, you need a cryptocurrency wallet to manage your cryptocurrency. Wallets monitor addresses on the blockchain and even update their own balance with each transaction.
An address is like your email address. It is something you provide to people who want to send you cryptocurrency.
Now that you know the why, let’s talk a bit about the how.
How Does a Wallet Work?
A cryptocurrency wallet, is an application with 3 main functions:
- Send and receive cryptocurrency
- Store cryptocurrency
- Monitor cryptocurrency balances
One of the most important things to remember about a wallet, is that this is where your private key is stored. In essence, a private key is just a very long string of numbers and letters that act as the password to your wallet.
You might be asking yourself, what are keys? Keys control access to your wallet.
There are 2 key types: private keys and public keys.
A public key is a unique code that acts like a digital address for your cryptocurrency wallet. It’s used to receive funds from other wallets. Similar to a bank account number, where it can be shared with others and money can be deposited into, but will not provide the sender access to your bank account.
You will typically be asked to generate a new public and private key pair, and the public key will be displayed as your wallet’s “receiving address.”

Private keys can be compared to your bank password that gives you access to authorize withdrawals. Because your private keys provide you with access to your cryptocurrency, they should never be shared with others or put online. Just like your online banking password, the private key is to be seen only by the person who owns the address to keep your currency safe.
We want to emphasize this statement. Just like your online banking password, your private key(s) should never be shared with anyone.
Wallet Categories
There are different wallets, and the type of wallet/s you use to hold your crypto will vary depending on your needs.
For this article, our goal is to provide a general understanding to help you recognize there are different types of wallets. So don’t worry if this leaves you a bit confused. We are here to help and in follow-up articles, we will provide additional content digging deeper into each one.
Let’s start with names of the most common wallet types:
- Chrome Extension Wallets
- Web Wallets
- Mobile Wallets
- Desktop Wallets
- Hardware Wallets
- Open Source vs Closed Source Wallets
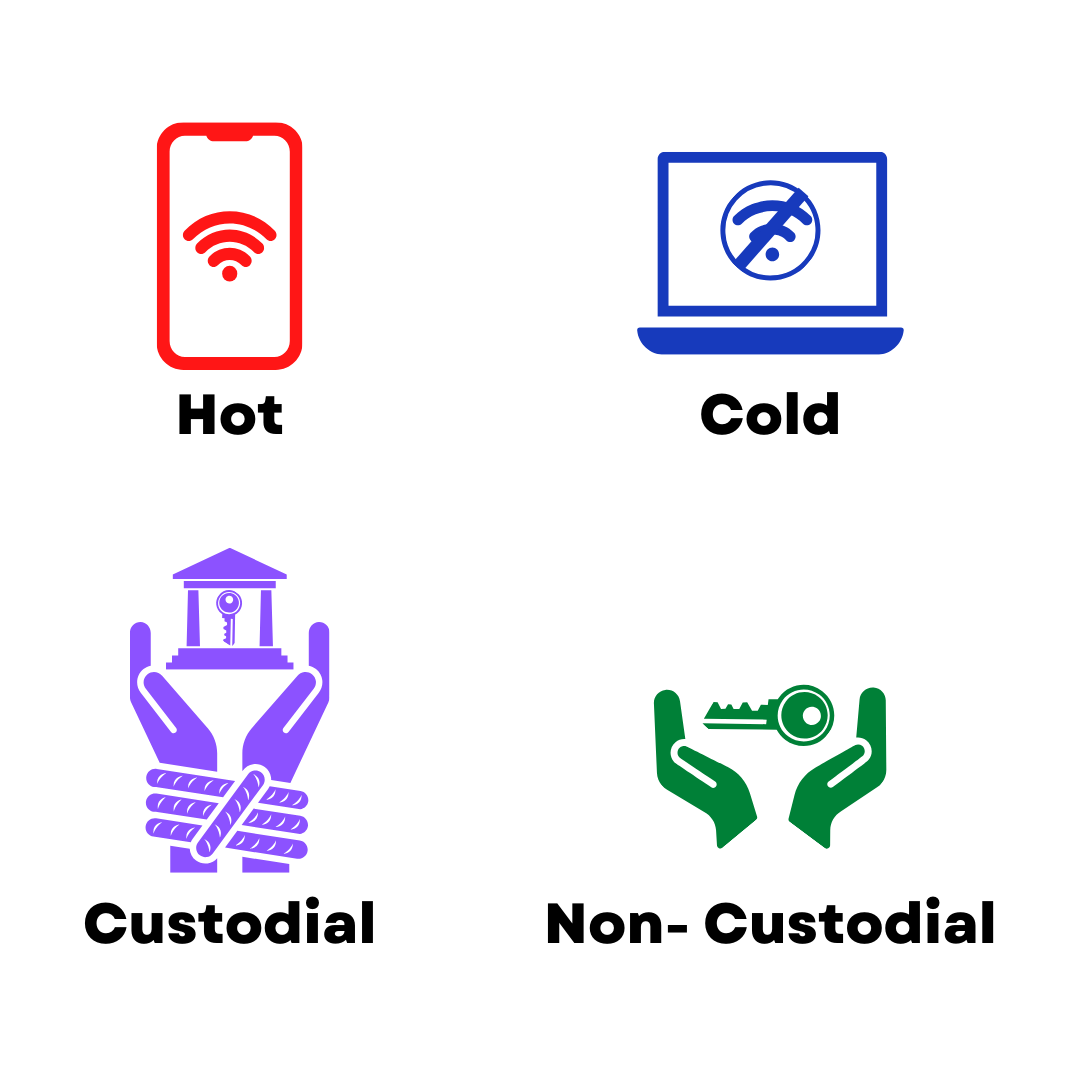
These wallets types will fall under 2 main categories:
Private Key Ownership
- Custodial — the wallet provider holds your private keys. These wallets are typically very easy to set-up and use (username/password), with the provider handling the technical details, for generating and securing the private keys. But although this does simplify set-up and use, it means the provider has control over your assets and if the wallet provider experiences a security breach or goes out of business, you could potentially lose access to your cryptocurrency
- Non-Custodial — also known as self-custody, are wallets where only you control the private key. This means that only you have access to your crypto assets and no one else. And with this great power comes great responsibility. You will need to understand how to safely secure and use your key. Unlike when you lose your password, there is no helpdesk to call to recover your access
Accessibility
- Hot — a wallet that is connected to the Internet. Think of this like a wallet you keep in your back pocket or purse. Easily accessible, but you wouldn’t put your life savings in it
- Cold — these wallets may also be commonly referred to hardware wallets. They are not connected to the internet and thus less accessible, because of this they are ideal for storing larger sums (less accessible to online threats, such as hackers)
In articles to follow, we will take you deeper into understanding of wallet types, how they work, how to choose a wallet and most importantly, the best practices for how to securely manage and use your cryptocurrency.
Our mission is to help you gain a good understanding of what cryptocurrency is and feel confident in how to use it safely.
Stay tuned for more content from C4’s Cryptocurrency Essentials Committee!
This article was written by our CryptoCurrency Essentials (CCE) Committee.
Disclaimer
The information presented in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It does not constitute financial advice, investment recommendations, or any form of endorsement.
The views and opinions expressed by individuals in this article are solely those of the speakers and do not necessarily represent those of C4 or any other organizations with which they are affiliated.
The mention or inclusion of any individuals, companies, or specific cryptocurrency projects in this video should not be considered as an endorsement or promotion.
Regulations and legal frameworks around cryptocurrencies may vary in different jurisdictions. It is your responsibility to comply with the applicable laws and regulations of your country or region.
