
Introduction
Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, have taken the world by storm. These unique digital assets are revolutionizing the way we think about ownership, value, and authenticity in the digital realm. From digital art to virtual real estate and gaming, NFTs offer a new way to own, trade, and monetize unique digital items. But for those new to the world of NFTs, understanding the basics can be daunting. In this article, we'll provide a comprehensive beginner's guide to NFTs, including what they are, how they work, and their potential applications and impact on the digital economy.
What are NFTs?
Non-fungible tokens, or NFTs, are unique digital assets that exist on a blockchain. They are used to verify ownership and authenticity of digital items such as artwork, videos, and tweets, among others.
Each NFT has a unique digital signature, which verifies its authenticity and ownership. This signature is recorded on the blockchain, making it immutable and tamper-proof. NFTs are created using smart contracts, which are self-executing programs that automatically enforce the terms of the agreement. Smart contracts are embedded in the NFT and can be programmed to include various conditions, such as royalties for the creator every time the NFT is resold.
NFTs are mostly associated with the Ethereum blockchain, as the ERC-721 standard was specifically designed for the creation and exchange of NFTs. This standard provides a common set of rules for developers to create unique digital assets that cannot be replicated or divided. However, they are also on other chains such as Polygon and even on Bitcoin through Counterparty and RSK which use smart contracts to emulate the functionality of ERC-721 standard on Bitcoin.
Some well known NFTs are Rare Pepes, a series of digital trading cards that were created as a tongue-in-cheek reference to the popular "Pepe the Frog" internet meme. The project was launched in 2016 by a group of Bitcoin enthusiasts who wanted to experiment with creating and trading unique digital assets on the Bitcoin blockchain.
How do NFTs work?
NFTs are minted on a blockchain, a decentralized ledger that ensures secure and transparent transactions. Each NFT possesses a unique digital signature verifying its authenticity and ownership. Once recorded on the blockchain, this signature becomes immutable, ensuring it's tamper-proof.".
NFTs can be bought, sold, and traded on various platforms, including online marketplaces such as OpenSea, Rarible, and SuperRare. These platforms allow users to create and sell their own NFTs, as well as browse and purchase NFTs from other creators.
One of the main use cases for NFTs is digital art. NFTs have opened up a whole new market for digital art, with some NFTs selling for millions of dollars. For example, "The First 5000 Days" by Beeple, a digital artwork as an NFT, sold for $69 million at a Christie's auction. Other examples of NFTs include virtual real estate in blockchain-based worlds, such as Decentraland, and virtual trading cards featuring sports stars.
NFTs also provide a new way for artists and creators to monetize their work and gain exposure. They offer a way for collectors to own and trade unique digital items that cannot be replicated.
What can you do with NFTs?
With NFTs, you can buy, sell, and trade unique digital items in a decentralized and secure way. You can also display your NFT collection on various platforms, including social media and digital galleries.
NFTs offer a new way to own and trade unique digital items, and they have the potential to create new revenue streams for artists and creators. For example, the digital art marketplace SuperRare allows artists to showcase and sell their NFTs as art to collectors. NFTs can also be used to represent in-game items, characters, and experiences in the gaming industry. The blockchain-based game Axie Infinity, for example, allows players to buy, sell, and trade NFTs representing creatures called Axies. From art to gaming, NFTs have demonstrated their potential, with some selling for as much as $300,000 and others even fetching into the millions.
How do NFT royalties work?
NFTs have the potential to generate royalties for their creators or original owners every time they are resold. This is made possible through smart contracts, which are embedded in the NFT and automatically execute the terms of the agreement.
For example, a smart contract can be set up to ensure that the original creator receives a percentage of the sale every time the NFT is resold. This allows creators to benefit from the value of their work, even after they have sold it. It also provides an incentive for collectors to hold onto their NFTs, as they can potentially increase in value over time.
How do you mint an NFT?
To mint an NFT, you need to create a unique digital item and upload it to a blockchain platform that supports NFTs. This process involves verifying the authenticity of the digital item and creating a smart contract that outlines the terms of the ownership and resale of the NFT.
There are several platforms that support NFTs, including Ethereum-based platforms such as OpenSea, Rarible, and SuperRare. Some platforms allow users to create and sell NFTs in just a few clicks, while others offer more advanced customization options.
What makes NFTs valuable?
The value of NFTs is largely based on their uniqueness and demand in the market. Some NFTs have sold for millions of dollars, and their value can fluctuate based on market demand, rarity, and historical significance. The value of an NFT can also be influenced by the fame of the creator, as well as the quality and originality of the digital item.
NFTs also provide a new way for artists and creators to monetize their work and gain exposure. They offer a way for collectors to own and trade unique digital items that cannot be replicated.
Are NFT’s only artwork?
NFTs are not just limited to the art world. In fact, they can represent any unique digital asset that can be stored on a blockchain. This versatility has opened up new possibilities for various industries, including DeFi, or decentralized finance.
Some examples of NFTs that are not artwork include virtual real estate, music, sports memorabilia, tweets, and in-game items and experiences. NFTs can be used to represent ownership and authenticity of any digital item that is unique and has value.
In the context of DeFi, NFTs can also be used to represent LP (liquidity provider) positions on decentralized exchanges such as Uniswap. LP tokens represent a share in a liquidity pool that contains a certain amount of two different tokens. These LP tokens can be traded or sold on various platforms.
NFTs can be used to represent LP tokens, allowing users to trade and transfer their LP positions in a decentralized and secure way. This provides a new way for users to monetize their LP positions and participate in various yield farming and liquidity provision opportunities that exist on decentralized exchanges.

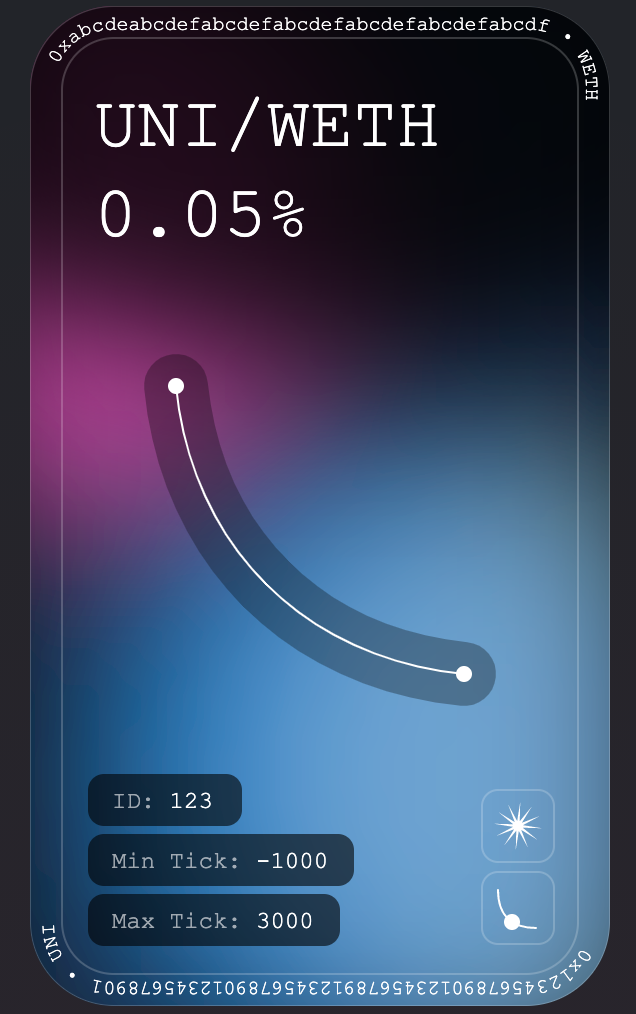
There are even NFT-based projects that are focused on LP positions and yield farming, such as Uniswap and Velodrome. These platforms allow users to trade and fractionalize their LP tokens, creating a new market for liquidity provision and yield farming strategies.
Overall, NFTs are a versatile and exciting technology that have the potential to revolutionize the way we think about ownership and value in various industries.
The future of NFTs
As the market for NFTs continues to grow, the potential applications and impact on the digital economy are vast. NFTs have the potential to revolutionize the art world, create new revenue streams for game developers, and provide a way for collectors to own and trade unique digital items. The gaming industry is particularly ripe for the growth of NFTs, with blockchain-based games and virtual worlds providing a new way for players to own and trade in-game items and experiences.
Conclusion:
The future of NFTs is exciting and full of potential. As the technology continues to evolve, we are likely to see even more innovative uses and applications of NFTs in various industries. From art and music to gaming and DeFi, NFTs offer a new way to own, trade, and monetize unique digital assets.
In the popular movie "Ready Player One," digital assets play a central role in the story's plot. The film envisions a future where digital currencies are used as a form of currency in a virtual world, where users can own and trade unique digital items and experiences. While this may seem like a far-fetched idea, it's not too far from reality. The gaming industry is already exploring the use of NFTs to represent in-game items and experiences, and the potential for NFTs to become a new form of currency is not too far-fetched.
In the context of "Ready Player One," the OASIS operates on a blockchain-like system, where users can buy, sell, and trade unique digital items. The rare Easter egg that Wade Watts is searching for is essentially a unique digital asset that grants ownership of the virtual world which is just like an NFT to show ownership of a particular digital asset.
As we look to the future of NFTs, it's important to stay informed and educated about the latest developments and potential applications. NFTs offer a new way to think about ownership and value in the digital realm, and they have the potential to disrupt various industries and create new opportunities for creators and collectors alike.
This article was written by our CryptoCurrency Essentials (CCE) Committee, with special thanks to committee member RJ Ricasata.
Other CCE Committee articles:
Secure Your Crypto: A Guide to Different Wallet Types
Safeguarding Your Crypto Legacy: Best Practices for Cryptocurrency Inheritance Planning
Exchange/Custodial Wallet Pros and Cons
Additional Resources:
Prep Books (Digital Downloads)
Disclaimer
The information presented in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It does not constitute financial advice, investment recommendations, or any form of endorsement.
The views and opinions expressed by individuals in this article are solely those of the speakers and do not necessarily represent those of C4 or any other organizations with which they are affiliated.
The mention or inclusion of any individuals, companies, or specific cryptocurrency projects in this video should not be considered as an endorsement or promotion.
Regulations and legal frameworks around cryptocurrencies may vary in different jurisdictions. It is your responsibility to comply with the applicable laws and regulations of your country or region.
